|
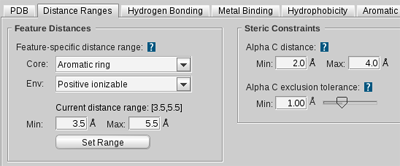
Feature-specific distance range
|
Defines the distance interval in which LigandScout
considers hydrogen bonding by
Hydrogen
Bond Donor
and
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor
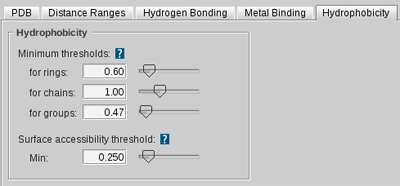
features, hydrophobic interactions by
Hydrophobic
features, charge interactions by
Ionizable
features, metal binding interactions by
Magnesium
,
Zinc
, and
IronBinding Locations
,
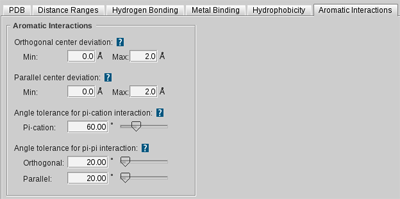
and aromatic interactions by
Aromatic Plane
features.
|
|
Core
|
Select the ligand-side feature for which the distance
constraint should be set.
|
|
Env
|
Select the environment-side feature for which the distance constraint
should be set. An interaction is only possible within the defined
distance range. The environment is the part of the macromolecule that
surrounds the ligand.
|
|
Current distance range
|
Shows the currently set distance range for the
selected core-environment feature pair.
|
|
Min
|
Adjust the minimum distance range. (in ┼)
|
|
Max
|
Adjust the maximum distance range (in ┼).
|
|
Set Range
|
Sets the newly adjusted distance range for the
selected core-environment feature pair.
|