Pharmacophore Feature Definitions
LigandScout provides the following pharmacophore
features for automated pharmacophore generation:
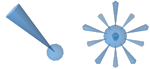
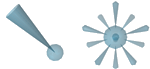
While hydrogen bond features are defined by direction and
distance constraints, hydrophobic interactions and ionizable areas
have a distance constraint only. Dedicated features are supplied
for the characterization of the binding of ligands to magnesium,
zinc and iron. In addition to LigandScout's supported chemical
features, the program increases selectivity of the generated
pharmacophores with the
Excluded Volume Feature
.
During pharmacophore generation, LigandScout analyzes the shape of
the active site and places
excluded volume spheres
in positions that are sterically claimed by the macromolecular
environment. This process ensures that molecules retrieved via virtual
screening match the sterical requirements of the active site while
simultanously drastically increasing selectivity.
Excluded volume coats
are likely to further increase enrichment.
Pharmacophore Feature Constraint Types
Pharmacophore features are defined by
following constraints types:
Distance Constraints
represent the relation between two points, one located on the ligand
side, one on the macromolecular side.
The following table shows LigandScout's default distance
constraint settings:
Direction Constraints
represent the
relationship between two atom groups, one located on ligand side, one
on macromolecular side. Groups form a rigid reference geometry,
which are the basis for a directed vector.
Pharmacophore Feature Definitions
LigandScout discriminates flexible against rigid hydrogen
bonds.
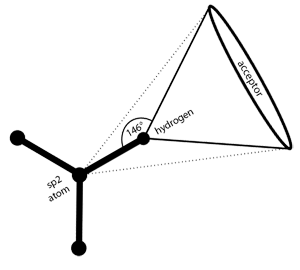
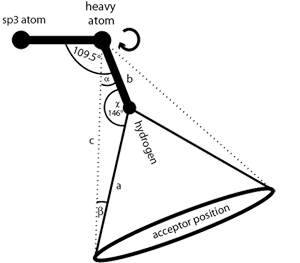
Rigid H-bond interactions, as occurring at sp
2
hybridized
heavy atoms, are represented by a cone with cutoff apex. The
default angle range for sp
2
hybridized heavy atoms is 50 degrees.
See
the section called “Hydrogen Bonding”
for detailed instructions.
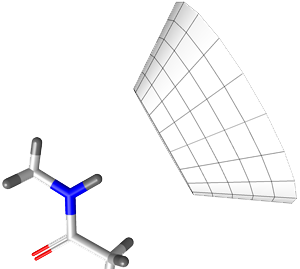
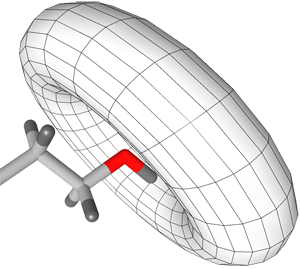
Flexible H-bond interactions, as occurring at sp
3
hybridized
heavy atoms, are represented by a torus. The default angle range
for sp
3
hybridized heavy atoms is 34 degrees. See
the section called “Hydrogen Bonding”
for detailed instructions.
Metal Binding Features (Magnesium, Zinc and Iron)
The maximum binding direction deviation for metal binding
groups is 120 degrees; the respective binding symmetry deviation is
0.75 ┼.
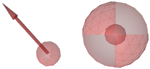
Charge Interaction Features
Charge interactions are considered to be distance constraints
and are depicted as an astral center in LigandScout.
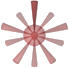
Consistent with charge interaction features, also
hydrophobicity features are regarded as distance constraints and
are represented as a single sphere in LigandScout. Minimum
thresholds and surface accessability thresholds are user-adaptable.
See
the section called “Hydrophobicity”
for detailed instructions.
Aromatic features represent pi-pi (orthogonal & parallel)
and cation-pi interactions. LigandScout identifies aromatic systems
of the ligand that are interacting with aromatics or cations in the
environment. See
the section called “Aromatic Interactions”
for detailed instructions.
Excluded volumes are derived from the sterical circumference
of the macromolecule. LigandScout analyzes shape of the active site
and places excluded volume spheres in positions that are sterically
claimed by the macromolecular environment. Excluded volumes spheres
are represented as single spheres in LigandScout. LigandScout's
default settings are user-adaptable. See
the section called “Distance Ranges”
for detailed instructions.