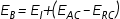Calculation of MMFF94 Binding Enthalpies
When a molecule library has been loaded, the library menu entry
Calculate MMFF94 Binding Enthalpy
allows the calculation of MMFF94 based energies that quantitatively describe the interaction of the
library molecules with the surrounding structural environment of the binding pocket (if present).
The thus calculated binding enthalpies can for example be used to establish a ranking of ligand
tautomers regarding their “relevance” for later pharmacophore modeling and investigation of putative
binding modes.
The MMFF94 binding enthalpy
E
B
for a molecule relative
to its surrounding macromolecular environment is calculated by the following formula:
Where
E
AC
is the computed strain-energy of the molecule in its refined active
conformation,
E
RC
is the energy of the geometry optimized molecule
in a relaxed conformation (local minimum) and
E
I
is the ligand-protein
interaction energy (sum of intermolecular Coulomb and Van der Waals terms).
All of these energy contributions get calculated by the MMFF94 force field.
As the above equation shows, the calculated energy for a given ligand molecule conformation consists
of two contributions: The term
E
AC
- E
RC
,
which represents the internal strain imposed by the transition from a local energetic minimum to
the active conformation, and
E
I
,
which is the gain in energy due to Coulomb and Van der Waals interactions of the ligand molecule
with the binding-pocket. Thus the lower the calculated binding enthalpy for a molecule (a
positive value means that energy must be supplied to the system for the formation of the ligand-protein
complex) the more energetically favorable is its interaction with the macromolecular environment relative
to other molecules with higher energies. Note that the formation of a strong ligand/macromolecule
complex is also influenced by entropical effects which are not regarded in the calculation of the binding enthalpy!